Boeing capsule lands back on Earth after space shakedown
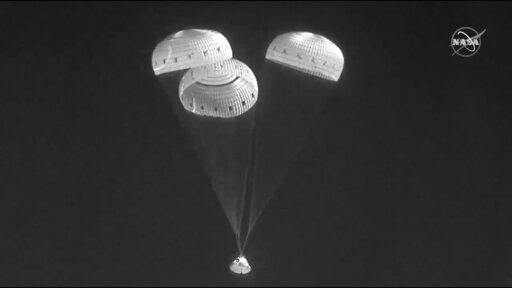
In this infrared image from video made available by NASA, the Boeing Starliner capsule uses parachutes as it descends from space to land at the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico on Wednesday, May 25, 2022. (NASA via AP)
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — Boeing’s crew taxi returned to Earth from the International Space Station on Wednesday, completing a repeat test flight before NASA astronauts climb aboard.
It was a quick trip back: The Starliner capsule parachuted into the New Mexico desert just four hours after leaving the orbiting lab, with airbags attached to cushion the landing. Only a mannequin was on board.
Aside from thruster failures and cooling system snags, Starliner appeared to clinch its high-stakes shakedown cruise, 2 1/2 years after its botched first try.
NASA astronauts will strap in next for a trip to the space station. The space agency has long wanted two competing U.S. companies ferrying astronauts, for added insurance as it drastically reduced its reliance on Russia for rides to and from the space station.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX is already the established leader, launching astronauts since 2020 and even tourists. Its crew capsules splash down off the Florida coast, Boeing’s Starliner returns to the Army’s expansive and desolate White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico.
Boeing scrapped its first attempt to reach the space station in 2019, after software errors left the capsule in the wrong orbit and nearly doomed it. The company fixed the flaws and tried again last summer, but corroded valves halted the countdown. Following more repairs, Starliner finally lifted off from Cape Canaveral last Thursday and docked to the space station Friday.
Station astronauts tested Starliner’s communication and computer systems during its five days at the space station. They also unloaded hundreds of pounds (kilograms) of groceries and other supplies that flew up in the Boeing capsule, then filled it with empty air tanks and other discarded gear.
A folded U.S. flag sent up by Boeing stayed behind, to be retrieved by the first Starliner crew.
“We’re a little sad to see her go,” station astronaut Bob Hines radioed as the capsule flew away.
Along for the ride was Starliner’s test dummy — Rosie the Rocketeer, a takeoff on World War II’s Rosie the Riveter.
The repairs and do-over cost Boeing nearly $600 million.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.