Anxiety at NASA as Mars InSight spacecraft nears Red Planet
NASA’s Mars Insight spacecraft launched nearly seven months ago with the goal of listening for quakes and tremors to see how the Red Planet formed billions of years ago (Gal ROMA)
Los Angeles (AFP) – Seven years of work and a journey of nearly seven months were about to be capped by almost seven minutes of terror as NASA ticked off the final hours to the high-drama landing of its $993 million Mars InSight spacecraft on Monday.
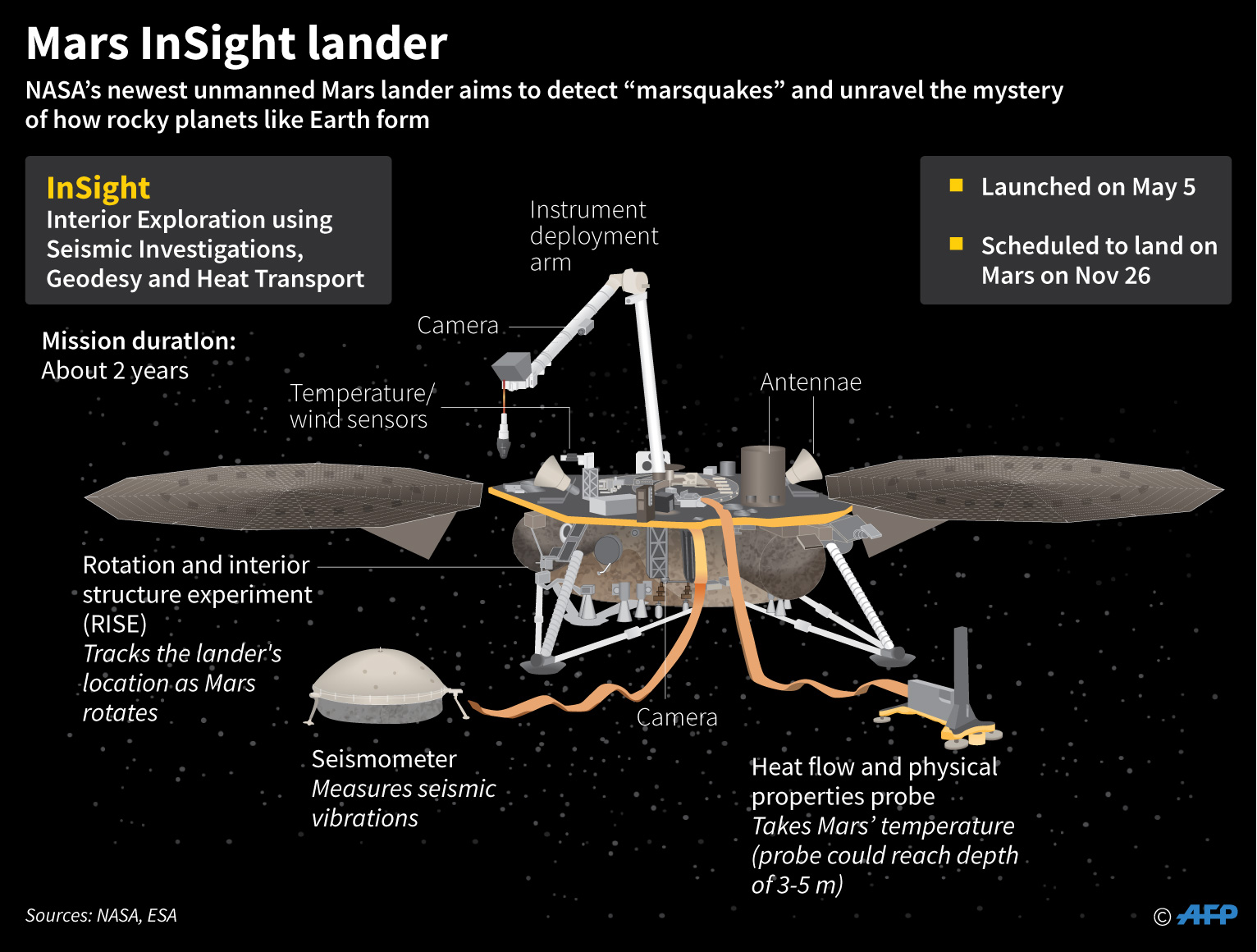
Mars InSight’s goal is to listen for quakes and tremors as a way to unveil the Red Planet’s inner mysteries, how it formed billions of years ago and, by extension, how other rocky planets like Earth took shape.
The unmanned spacecraft is NASA’s first to attempt to touch down on Earth’s neighboring planet since the Curiosity rover arrived in 2012.
More than half of 43 attempts to reach Mars with rovers, orbiters and probes by space agencies from around the world have failed.
NASA is the only space agency to have made it, and is invested in these robotic missions as a way to prepare for the first Mars-bound human explorers in the 2030s.
“We never take Mars for granted. Mars is hard,” said Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA associate administrator for the science mission directorate, on Sunday.
– ‘An absolutely terrifying thought’ –
The nail-biting entry, descent and landing phase begins at 11:47 am (1940 GMT) at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, home to mission control for Mars InSight.
A carefully orchestrated sequence — already fully preprogrammed on board the spacecraft — takes place over the following several minutes, coined “six and a half minutes of terror.”
Speeding faster than a bullet at 12,300 miles (19,800 kilometers) an hour, the heat-shielded spacecraft encounters scorching friction as it enters Mars’ atmosphere.
The heat shield soars to a temperature of 2,700 Fahrenheit (about 1,500 Celsius). Radio signals may be briefly lost.
The heat shield is discarded, the three landing legs deploy, and the parachute pops out.
“We freefall for just a little bit, which is an absolutely terrifying thought for me,” said Tom Hoffman, project manager of InSight.
But then the thrusters begin to fire, further slowing down the 800-pound (365 kilogram) spacecraft to a speed of just about 5 mph when it reaches the surface.
Since there is no joystick back on Earth for this spacecraft, and no way to intervene if anything goes wrong, Hoffman described his emotions as mixed.
“I am completely comfortable and completely nervous at the same time,” he said.
“We have done everything we can think to make sure we are going to be successful, but you just never know what is going to happen.”
Hoffman added that he has “not been sleeping that great,” though he said that might be because of his rambunctious toddlers, who are two and four years old.
When the first signal arrives at 2001 GMT, hopefully showing that the lander set itself down, intact and upright, “I am totally going to unleash my inner four-year-old at that point,” he said.
– Goal: 3D map of inner Mars –
Zurbuchen described InSight as “unique” because the waist-high lander contains instruments that were contributed by several European space agencies.
France’s Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) made the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) instrument, the key element for sensing quakes.
The German Aerospace Center (DLR) provided a self-hammering mole that can burrow 16 feet (five meters) into the surface — further than any instrument before — to measure heat flow.
Spain’s Centro de Astrobiologia made the spacecraft’s wind sensors.
Other significant contributions to the project came from the Space Research Center of the Polish Academy of Sciences and Astronika, the Swiss Institute of Technology, and Britain’s Imperial College London and Oxford University.
Together, these instruments will study geological processes, said Bruce Banerdt, InSight’s principal investigator at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
By listening for tremors on Mars, whether from quakes or meteor impacts or even volcanic activity, scientists can learn more about its interior and reveal how the planet formed.
The goal is to map the inside of Mars in three dimensions, “so we understand the inside of Mars as well as we have come to understand the outside of Mars,” Banerdt told reporters.
NASA made one final course correction late Sunday.
With the rest of the landing sequence all pre-programmed, all NASA scientists can do is cross their fingers and hope for the best.
Coverage on the NASA website begins at 11:00 am (1900 GMT).
Disclaimer: This story has not been edited by Siliconeer and is published from a syndicated feed. Siliconeer does not assume any liability for the above story. Validity of the above story is for 7 Days from original date of publishing. Content copyright AFP.